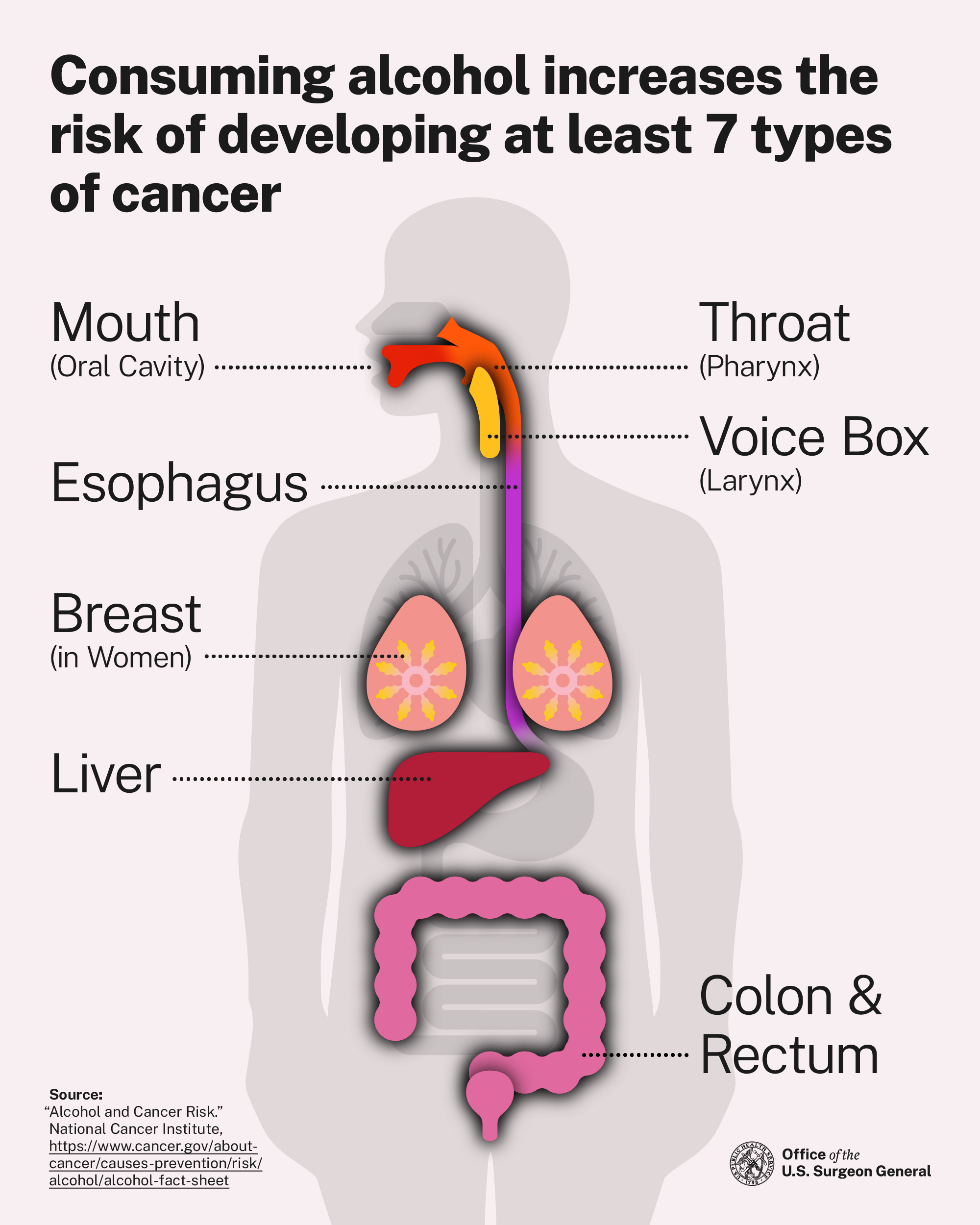
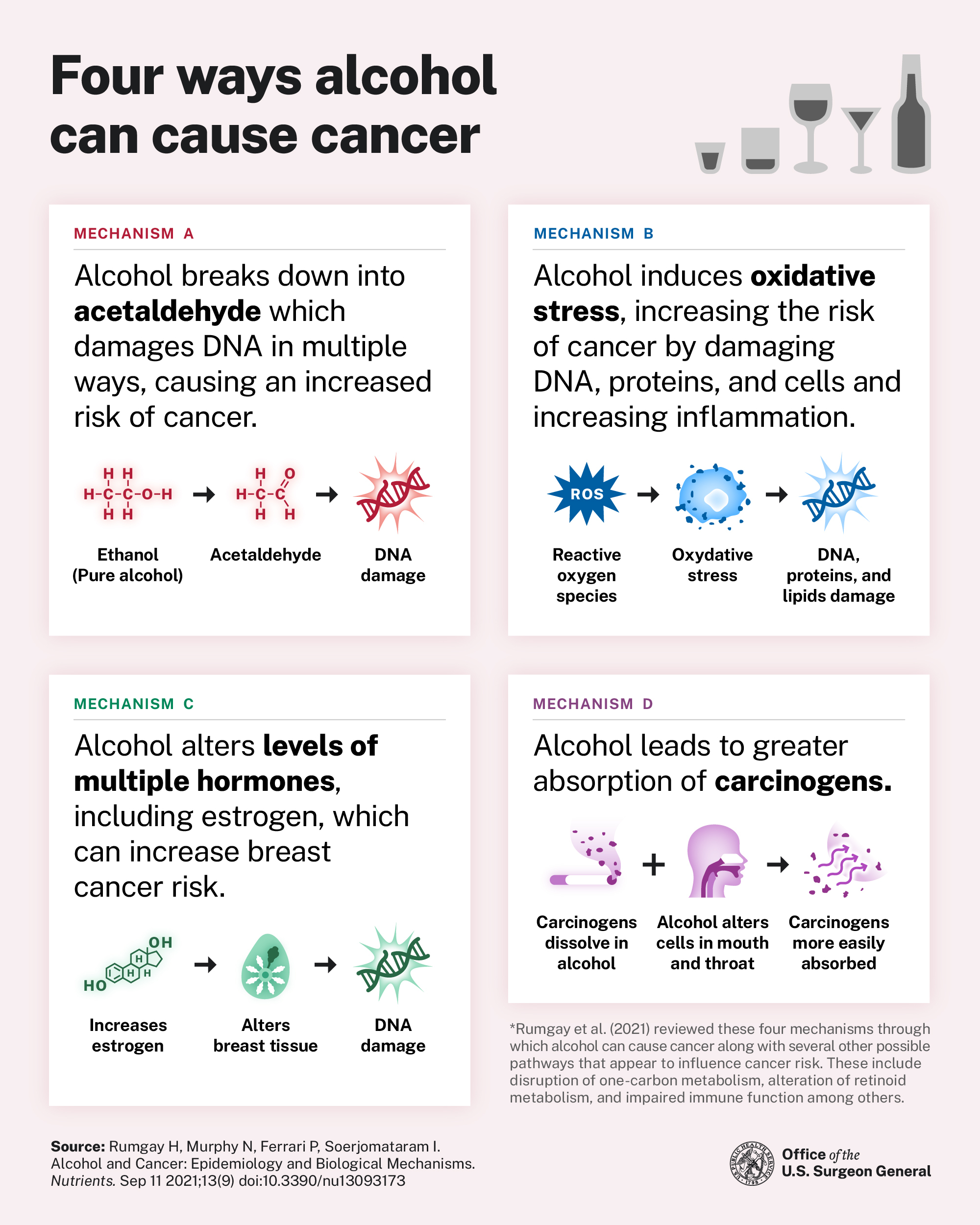
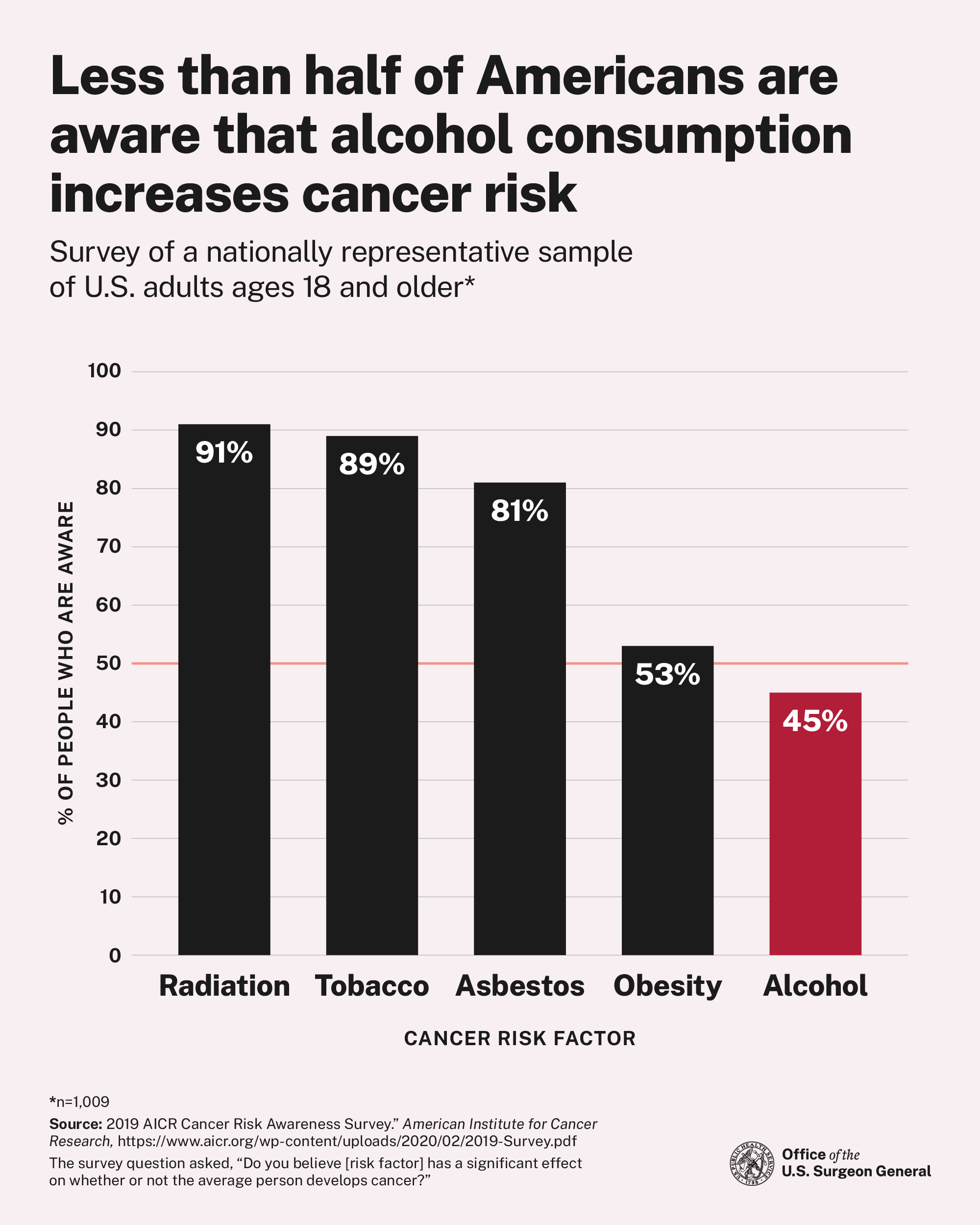
This Advisory describes the scientific evidence for the causal link between alcohol consumption and increased risk for at least seven different types of cancer, including breast (in women), colorectum, esophagus, voice box, liver, mouth, and throat. The Advisory also helps to better inform the public of this relationship and offers key recommendations to reduce alcohol-related cancers.
Spread the word with these shareable resources
Additional Resources
Lifeline Resources
Rethinking Drinking and Check Your Drinking
The National Institute on Alcohol Abuse and Alcoholism’s Rethinking Drinking initiative offers ways to evaluate your drinking and decide whether and how to make a change. In addition, CDC offers a free, interactive tool for you to check your drinking and get personalized feedback (in English and Spanish). Additionally, there are some individuals – PDF who should not drink at all.
“Talk. They Hear You.”
SAMHSA’s “Talk. They Hear You.” campaign offers tips on how to talk to children and youth about alcohol.